Web Service (HTTPs)
TRASAGATE web proxy controls access to web applications (HTML5) with policies, two-factor authentication without changing a single line of code in your application.
How does it work?
TRASAGATE web access-proxy works a bit differently than SSH and RDP services. Your browser should send all HTTPs traffic of your upstream service to the TRASAGATE server. Once policy validations are completed, TRASAGATE forwards those HTTPs requests to the upstream webserver. For this, you will need to obtain a domain name for upstream service and point DNS to the TRASAGATE server IP address.
Prerequisites
- A domain name for web service which points to TRASAGATE (should be a subdomain of TRASAGATE server A record)
- IP or domain name of primary web service (where TRASAGATE access proxy will forward incoming requests)
Users will need to install the TRASAGATE browser extension in their browsers to access the HTTPs service.
In this guide
- Gitlab is hosted in IP
10.10.0.10. - We have set the domain name
gitlab.Trasagate.com, which points to the IP of the TRASAGATE server. - When users visit
gitlab.Trasagate.com, their browser sends a request to the TRASAGATE server. When the TRASAGATE server receives a request forgitlab.Trasagate.comIt checks policies and forwards traffic to GitLab server's origin IP10.10.0.10.
Creating Web Service Profile
Create a new service selecting http as the service type.
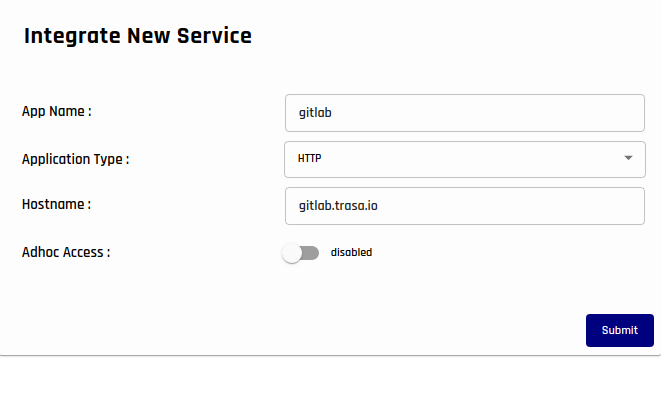
This is how your newly created service profile page look like.

Configuring Proxy setting.
We've configured the http service profile for GitLab to listen on domain gitlab.Trasagate.com. If you also have set up your DNS server that points the domain to the TRASAGATE server IP address, your users will be redirected to TRASAGATE server when they visit gitlab.Trasagate.com. But how will TRASAGATE server know where to forward the request once validation is processed?

Click the edit icon on Proxy Setting and enter the upstream server address in the designated field. In our case, we have added IP address 10.10.0.10 because that is where the actual GitLab server is running.
Now, when HTTP requests gitlab.Trasagate.com come to TRASAGATE server, it validates policies and performs authorization, and if everything is successful, it will forward the traffic to IP 10.10.0.10.